
They can show changes in the blood vessels near the ears and determine whether an underlying medical condition is causing symptoms. Imaging tests can also help doctors evaluate pulsatile tinnitus. Why do I need a MRI scan for tinnitus?Īn MRI scan may reveal a growth or tumor near the ear or the eighth cranial nerve that could be causing tinnitus. An MRI scan may reveal a buildup of fluid or inflammation in the inner ear or a growth on the nerve. MRI scans use a magnetic field and radio waves to create computerized, three-dimensional images of the ear and the nerve that carries signals from the inner ear to the brain.
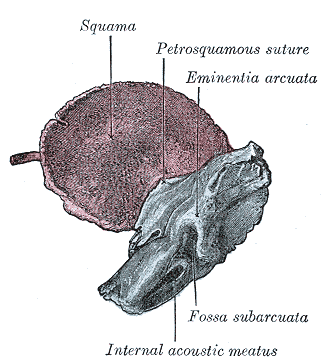
The internal acoustic canal (IAC), also known as the internal auditory canal or meatus (IAM), is a bony canal within the petrous portion of the temporal bone that transmits nerves and vessels from within the posterior cranial fossa to the auditory and vestibular apparatus. Where does the internal acoustic meatus lead to? The adult human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about 2.5 centimetres (1 in) in length and 0.7 centimetres (0.3 in) in diameter. What is meatus of ear?Īnatomical terminology The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear.
#AUDITORY MEATUS SKIN#
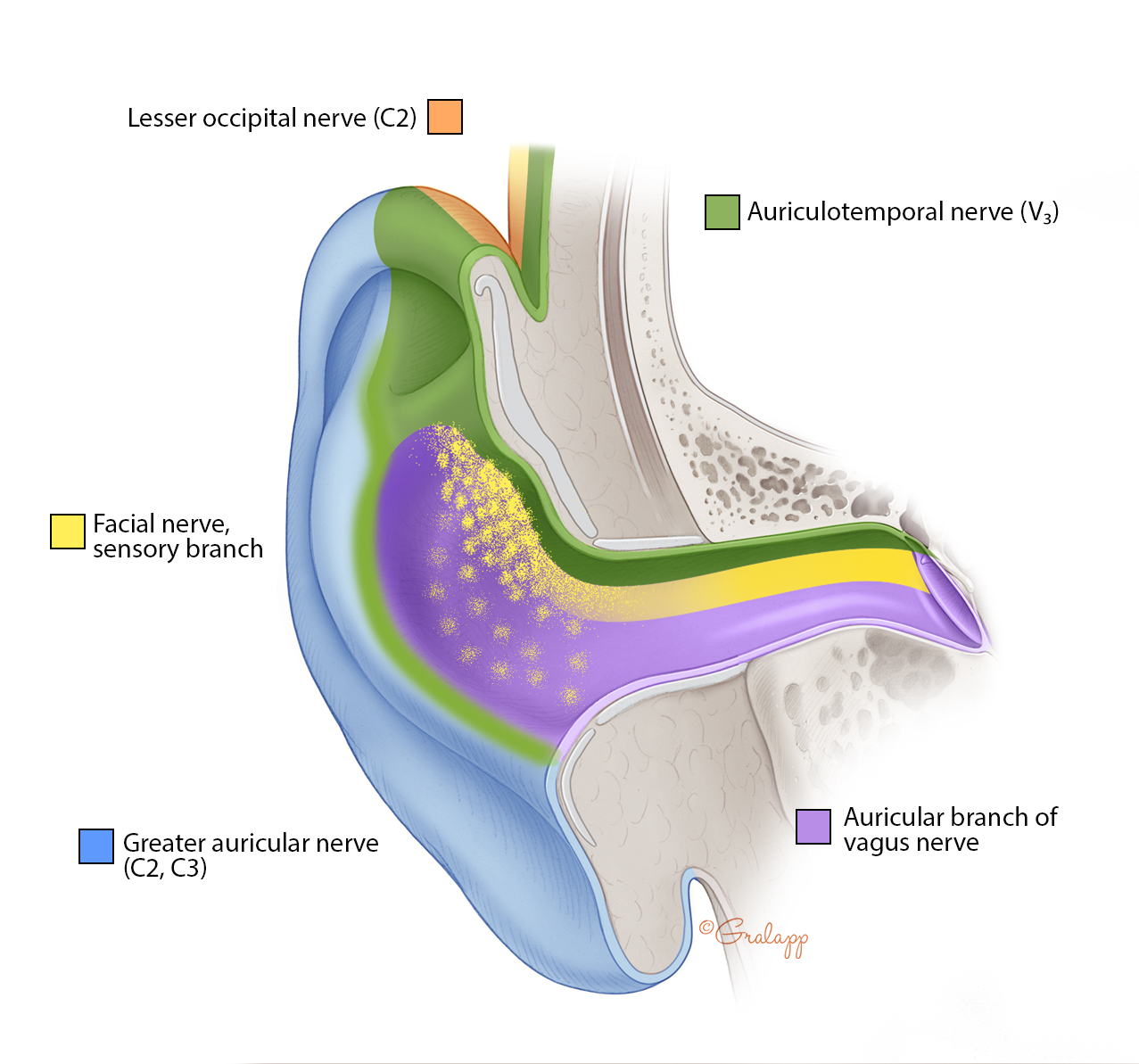
… The canal is nearly 1 inch (2.5 cm) in length and is lined with skin that extends to cover the tympanic membrane. What is the auditory meatus?Įxternal auditory canal, also called external auditory meatus, or external acoustic meatus, passageway that leads from the outside of the head to the tympanic membrane, or eardrum membrane, of each ear. If hearing loss affects one ear and not the other, called unilateral hearing loss, and if the results of hearing tests indicate that sensorineural hearing loss may be causing your symptoms, doctors may recommend an MRI scan to visualize the inner ear and surrounding structures. As the tumor expands, hearing loss may worsen, facial weakness may occur, and balance problems (disequilibrium) may occur. Small tumors, which are typically limited to the bony canal, cause hearing loss in one ear, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and unsteadiness or dizziness. Read More: What is substantia Innominata? What would be a potential symptom if a patient developed a tumor at the internal auditory meatus? The nervus intermedius is a branch of the facial nerve located posteriorly to the facial nerve and anterior to the superior vestibular nerve in the internal auditory canal. The facial nerve exits the internal auditory canal at the meatal foramen and continues towards the geniculate ganglion as the labyrinthine segment. Does facial nerve go through internal auditory meatus? What is a internal auditory meatus both?Īnatomical terms of bone The internal auditory meatus (also meatus acusticus internus, internal acoustic meatus, internal auditory canal, or internal acoustic canal) is a canal within the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull between the posterior cranial fossa and the inner ear. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the internal auditory canal (IAC) is a non-invasive, painless diagnostic imaging procedure that uses using radio waves and a strong magnetic field to create detailed images of the bony canal that transmits nerves and blood vessels from the base of the brain to the inner ear. An IAM MRI scan is a useful type of MRI for investigating symptoms of earache, dizziness, tinnitus and problems with balance. What is a MRI internal auditory meatus both for?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
